- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping

Sustainable Packaging: A Step Towards a Greener Future

Introduction
In a world increasingly threatened by climate change, pollution, and resource depletion, the need for sustainable practices has never been more urgent. One of the most impactful yet often overlooked areas where sustainability can make a real difference is packaging. From plastic wrappers to oversized cardboard boxes, traditional packaging methods contribute significantly to environmental damage. These materials often end up in landfills or oceans, taking decades or even centuries to decompose. In response, industries across the globe are embracing sustainable packaging a movement focused on reducing waste, conserving resources, and minimizing environmental harm through smarter material use and design. Sustainable packaging goes beyond simply replacing out plastic to paper. It represents a comprehensive approach that involves selecting renewable, biodegradable, or recyclable materials, using minimal resources during manufacturing, and ensuring packaging can be reused or easily disposed of at the end of its life. Whether it’s through compostable containers, recycled cardboard, or some design innovations, the goal is to reduce the ecological footprint while maintaining product safety, branding, and consumer convenience. A powerful example of this shift can be seen in the image of flip-flops displayed using minimalist, eco-conscious packaging. Designed by Avery Dennison, a global leader in packaging innovation, this display eliminates unnecessary layers and highlights how even simple, everyday products can contribute to a more sustainable future when packaged thoughtfully. It not only reduces material waste but also enhances shelf appeal proving that sustainability and style can go hand in hand.
What is Sustainable Packaging?
Sustainable packaging is an approach of developing and using packaging materials in a way that minimizes the environmental impact throughout the product’s lifecycle. It aims to reduce the ecological footprint of packaging by prioritizing more renewable, recyclable, or biodegradable materials, optimizing the design to minimize waste, and encouraging reuse or efficient disposal. Unlike conventional packaging, which relies on plastics and non-renewable resources, sustainable packaging mainly focuses on long-term environmental health and resource conservation.
At its core, sustainable packaging involves three key principles, that are: reducing waste, reusing materials where possible, and ensuring recyclability or composability. It looks at the entire lifecycle of a product from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing, using, and end-of-life disposal to find opportunities for minimizing harm to the environment. This holistic view ensures that packaging not only serves its functional purpose of protecting and transporting goods but also aligns with ecological and social responsibility. Materials used in sustainable packaging include recycled paper cardboard, bioplastics made from corn or sugarcane, plant-based fibers such as jute or hemp, and even innovative options like mushroom-based or seaweed-based packaging. These materials are either renewable or decompose naturally, unlike plastic which can persist in the environment for hundreds of years.
But sustainable packaging isn’t just about materials design also plays a critical role too. Packaging can be made more sustainable by reducing excess layers, avoiding mixed materials (sometimes which are harder to recycle), and designing for reuse or easy recycling. Clear labeling and disposal instructions also help consumers make environmentally friendly choices after use.
It also supports broader goals such as reducing carbon emissions, conserving energy and water in production, and supporting circular economy principles. Businesses adopting this approach often see added benefits including improved brand image, consumer loyalty, and compliance with environmental regulations.
Ultimately, sustainable packaging is all about balancing environmental responsibility with practical functionality. It’s not merely just a trend, but a necessity in the time of rising pollution and climate challenges. As industries are move toward greener solutions, sustainable packaging offers a powerful way to reduce harm without compromising performance or aesthetics.
Why Sustainable Packaging is Necessary?
Sustainable packaging has become a pressing necessity in today’s world due to the profound environmental, social, and economic impacts of conventional packaging practices. For decades, the global economy has relied heavily on plastic and non-recyclable materials for packaging products that are often used briefly but take centuries to decompose. This reliance has led to a staggering accumulation of waste in landfills, oceans, and natural ecosystems. These materials not only pollute the environment but also threaten wildlife, contaminate water bodies, and release microplastics into the food chain, ultimately affecting human health. As such, shifting toward sustainable packaging is no longer a luxury or a corporate trend; it is a global necessity for preserving life and the planet. In addition to environmental damage, traditional packaging also drains valuable natural resources. The production of plastic packaging relies on petroleum, a non-renewable resource, and consumes vast amounts of energy and water. The carbon emissions generated during the manufacturing and transportation contribute heavily to climate change. On the other hand, sustainable packaging aims to reduce this carbon footprint by using materials that are biodegradable, recyclable, or derived from renewable sources. By doing so, it helps conserve energy, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and protect natural resources.
There is also a growing demand from consumers for businesses to adopt more environmentally responsible practices as now a days consumers are also focusing on the sustainability. Today’s consumers are more informed and environmentally conscious than ever before. They are increasingly inclined to support brands that demonstrate sustainability and social responsibility. Companies that fail to adapt to this change risk losing relevance in the marketplace. On the contrary, businesses that embrace sustainable packaging not only reduce their ecological footprint but also enhance their brand image, attract eco-conscious customers, and foster long-term loyalty. In many markets, sustainable packaging has become a unique selling proposition, offering brands
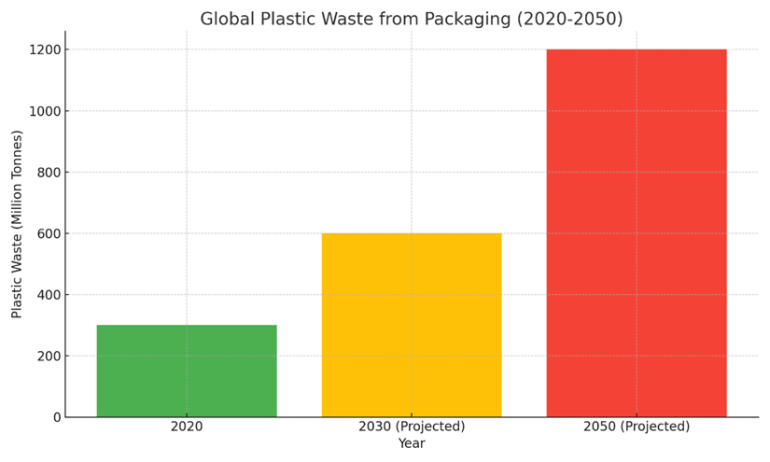
Figure 1: Global Plastic Pollution by Packaging
Source: Sustainable Packaging Industry Statistics: Market Data Report 2024
Government regulations and global policy initiatives have also accelerated the need for sustainable packaging. Countries around the world are implementing strict environmental laws, banning certain types of plastic, and setting ambitious targets for waste reduction and carbon neutrality. Adopting sustainable packaging helps companies stay compliant with these regulations and avoid legal or reputational consequences. Furthermore, international efforts such as the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) emphasize responsible production and consumption. Sustainable packaging directly aligns with these global objectives, making it an essential strategy for organizations aiming to contribute to sustainable development and corporate social responsibility.
Table 1: Global Plastic Production & Packaging Share.
Source: AP Report, Busan South Korea.
| Year | Global Plastic Production (Mt) | % Used for Packaging |
| 2020 | 547 Mt | 32% |
| 2024 | ~430 Mt new production | – |
Another critical factor driving the need for sustainable packaging is its role in enabling a circular economy an economic model that focuses on keeping resources in use for as long as possible.Unlike the linear “take-make-dispose” model of traditional packaging, sustainable solutions are designed with the entire lifecycle in mind. They are created to be reused, recycled, or composted, thereby reducing the need for virgin materials and decreasing waste generation. This shift toward circularity not only benefits the environment but also creates new business opportunities, promotes innovation, and fosters sustainable economic growth.
Avery Dennison’s Commitment to Sustainable Packaging
Avery Dennison has emerged as a prominent force in promoting sustainable packaging practices on a global scale. Known for its expertise in labeling and materials science, the company has made sustainability a core pillar of its business strategy. Avery Dennison understands that packaging plays a significant role in environmental degradation, and it has taken proactive steps to address this challenge through innovation, collaboration, and long-term vision.
One notable example is the company’s use of eco-designed packaging solutions such as hanger-style flip-flop displays. These designs drastically reduce the need for plastic and bulky cardboard boxes, replacing them with flat, paper-based holders that are easier to recycle and more efficient to transport. Such innovations highlight how packaging can be both functional and environmentally friendly.
Beyond product design, Avery Dennison has committed to ambitious sustainability targets. By 2030, it aims to achieve net-zero carbon emissions and ensure that all packaging materials are either recyclable, reusable, or compostable. The company is also focused on eliminating deforestation from its supply chains and developing adhesives and label technologies that do not hinder recycling. The global sustainable packaging market is projected to grow significantly from $219.6B in 2020 to $518.3B by 2030.
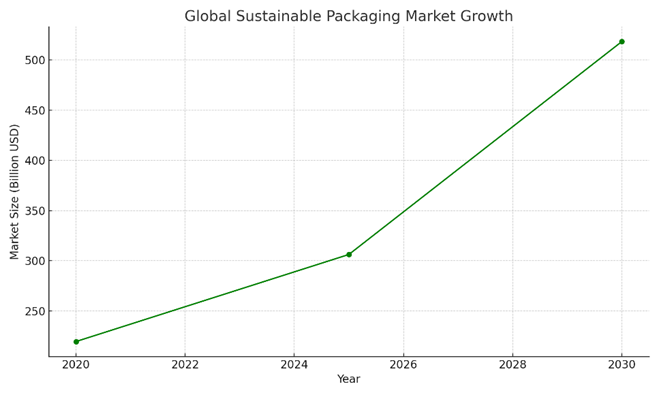
Figure 2: Avery Dennison 2030 Sustainability Targets
In addition to internal goals, Avery Dennison actively collaborates with global organizations to push industry-wide change. It partners with the Ellen MacArthur Foundation and supports circular economy initiatives that promote reuse and resource conservation. These efforts are supported by transparent reporting and public sustainability disclosures.
Avery Dennison’s approach is not limited to compliance or marketing—it is about driving real environmental progress. The company’s commitment is visible not just in its products, but in its investments, partnerships, and leadership in sustainable packaging. By making bold decisions today, Avery Dennison is paving the way for a packaging industry that balances performance with planetary well-being.
Core Materials Used in Sustainable Packaging
A wide range of materials is now being explored and adopted to replace conventional plastics and synthetics in packaging:
- Recycled Paper and Cardboard
- Bioplastics
- Mushroom-Based Packaging
- Bamboo and Jute
- Polylactic Acid (PLA)
Design Principles for Sustainable Packaging
Designing sustainable packaging requires a thoughtful balance between functionality, environmental responsibility, and user experience. One of the core principles is material efficiency using the least number of resources necessary without compromising the product’s protection or quality. This involves reducing excess layers, eliminating mixed materials that are difficult to recycle, and opting for renewable or biodegradable alternatives like recycled paper, bamboo, or bioplastics. Another essential element is end-of-life consideration. Packaging should be designed with a clear plan for what happens after use whether it can be composted, recycled, or repurposed. Simplicity is key; when packaging is intuitive and made from a single material, it’s more likely to be recycled correctly. Durability also plays a role, especially in reusable packaging systems, where the design must withstand repeated handling. Additionally, sustainable packaging should support efficient logistics. Flat or collapsible designs can reduce shipping volume and fuel consumption. Clear labeling and consumer instructions further enhance its impact by guiding proper disposal. Finally, good sustainable packaging maintains brand integrity and visual appeal, proving that eco-conscious choices don’t require aesthetic compromise. When these principles come together, the result is packaging that not only meets business and customer needs but also contributes meaningfully to reducing environmental harm.

Figure 3: Flip-flop paper hooks made of FSC environmentally friendly and renewable kraft cardboard.Source: www.mengcaii.com.
Benefits of Adopting Sustainable Packaging
Adopting sustainable packaging offers a wide range of benefits that extend beyond environmental impact. One of the most immediate advantages is the reduction in waste and pollution, especially from single-use plastics that often end up in landfills or oceans. By using recyclable, biodegradable, or reusable materials, companies significantly lower their ecological footprint. From a business perspective, sustainable packaging can lead to long-term cost savings through reduced material use, lighter shipping weights, and improved supply chain efficiency. It also enhances brand image and customer loyalty, as modern consumers increasingly prefer companies that prioritize environmental responsibility. Furthermore, sustainable packaging helps businesses stay compliant with growing global regulations and sustainability reporting requirements. It also opens doors to innovation, encouraging the development of creative packaging solutions that balance aesthetics with function. Overall, embracing sustainable packaging is not just good for the planet it’s a strategic move that strengthens a company’s position in a competitive, eco-conscious marketplace.
Challenges in Implementing Sustainable Packaging
While the shift toward sustainable packaging is gaining momentum, putting it into practice presents several complex challenges for businesses. One of the most common hurdles is the cost associated with eco-friendly materials. Biodegradable, recycled, or compostable alternatives often carry a higher price tag than traditional plastic or mixed packaging, which can strain budgets, especially for small and mid-sized companies. Supply chain limitations also play a role sourcing sustainable materials in large quantities or consistent quality can be difficult, particularly in regions where green infrastructure is underdeveloped.
Table 2: Recycling Rates by Material/Region.
Source: Reddit‑sourced EU data.
| Material | EU Recycling Rate (%) |
| Plastic Packaging | 41% (2019) |
| Paperboard/Metal | ~75% |
Another major challenge is recycling infrastructure, which varies widely from country to country and even city to city. A package that is recyclable in one area may end up in a landfill elsewhere due to a lack of proper facilities. Additionally, consumer behavior impacts the success of sustainable packaging. If customers aren’t informed or motivated to recycle properly, the benefits of eco-friendly materials may never be realized. There’s also the issue of design limitations, where sustainable materials might not offer the same durability, flexibility, or print quality required for certain products. Finally, navigating regulations and certifications related to sustainability can be confusing and time-consuming, especially for companies trying to align with multiple international standards. All these factors make the transition to sustainable packaging a challenging yet essential process that requires innovation, collaboration, and a long-term commitment.
Future Trends in Sustainable Packaging:
- Smart Packaging: One of the most promising developments in sustainable packaging is the rise of smart packaging technologies. By integrating QR codes, NFC tags, and other IoT-enabled features, companies can provide detailed information about the product’s origin, material composition, and proper disposal methods. These smart labels help consumers make informed choices and encourage responsible end-of-life behavior, such as recycling or composting. Additionally, smart packaging can track the product’s journey through the supply chain, helping brands improve transparency and reduce waste by identifying inefficiencies. This fusion of technology and sustainability is redefining how both businesses and consumers interact with packaging.
- Edible Packaging: Edible packaging is an exciting innovation that aims to eliminate waste altogether by creating packaging that can be safely consumed. Made from food-grade materials such as seaweed, rice paper, or potato starch, these solutions are particularly gaining attention in the food and beverage industry. Not only do they reduce reliance on single-use plastics, but they also offer a novel consumer experience. For items where eating the package isn’t practical, these materials are typically biodegradable and break down harmlessly in the environment. As research continues, edible packaging is expected to become more versatile, affordable, and widely accepted.
- Refillable Systems: Refillable packaging systems are gaining popularity as brands and consumers seek to minimize waste over the long term. Instead of disposing of packaging after one use, consumers are encouraged to refill containers at home or in-store using bulk stations or product pouches. This model significantly reduces the amount of packaging that ends up in landfills and promotes a circular economy. Refillable systems are already being adopted in industries like cosmetics, cleaning supplies, and beverages. With proper infrastructure and consumer incentives, this trend could revolutionize how everyday products are purchased and consumed.
- 3D-Printed Packaging: 3D printing is transforming sustainable packaging by enabling precise, on-demand production that eliminates excess material. This additive manufacturing process creates customized packaging tailored to the exact dimensions of the product, reducing the need for fillers and oversized boxes. Materials used in 3D printing can also be chosen for their recyclability or composability, further enhancing their environmental value. Because 3D printing supports local production and rapid prototyping, it also cuts down on transportation emissions and development time. As technology advances, 3D-printed packaging is likely to become more cost-effective and scalable across industries.
Sustainable Packaging and the Circular Economy in Fashion Industry
In the fashion industry, sustainable packaging is no longer an afterthought—it has become a vital part of a brand’s identity and environmental responsibility. With growing consumer demand for transparency and ethical practices, fashion businesses are rethinking how they deliver products without contributing to the global waste crisis. Packaging now plays a key role in advancing the circular economy within fashion. Brands are shifting from disposable plastic wraps and branded boxes to recyclable paper mailers, compostable bags, and reusable cloth pouches. Some forward-thinking labels even encourage customers to return packaging for reuse or recycling, creating closed-loop systems. Additionally, digital-first fashion companies are leveraging minimalist packaging with embedded QR codes that eliminate printed tags and brochures, reducing material use while enhancing the customer experience. These efforts align with broader circular economy goals by minimizing raw material extraction, extending the lifecycle of packaging, and preventing waste from entering landfills. By integrating sustainable packaging strategies into their operations, fashion brands are not only reducing their environmental impact but also strengthening their reputation, increasing customer loyalty, and staying competitive in a market that increasingly values purpose over profit.
Conclusion
Sustainable packaging is no longer a niche innovation it is a critical and strategic shift in how industries operate, communicate, and take responsibility for their environmental footprint. As this article has explored, the transition to sustainable packaging touches every stage of the supply chain, from material sourcing and product design to consumer engagement and end-of-life disposal. Whether it’s eliminating unnecessary plastic, designing for recyclability, or adopting circular systems, sustainable packaging enables businesses to align with growing consumer expectations and global environmental standards.
Avery Dennison’s leadership in this space offers a compelling example of how thoughtful innovation can reduce waste without sacrificing function or aesthetic value. Their hanger-style flip-flop packaging demonstrates how even the simplest design can deliver powerful environmental benefits. This shift is further amplified by emerging trends like smart packaging, refillable systems, edible materials, and 3D printing, which are expanding the possibilities for brands across all industries. However, as promising as sustainable packaging is, it comes with challenges ranging from higher costs and limited infrastructure to consumer awareness and regulatory hurdles. Yet, with each challenge comes an opportunity for innovation, collaboration, and long-term growth.
Ultimately, sustainable packaging is more than a design solution it is a commitment to stewardship, accountability, and forward-thinking business. As companies adopt this mindset, they are not only reducing their ecological impact but also building stronger, more resilient brands in a world that increasingly values sustainability. By embedding these principles into product strategy, packaging can serve not just as a protective shell, but as a powerful tool for environmental progress and brand transformation.
Author: Kumail Hasan, National Institute of Fashion Technology, Patna.
